EVA: Polyethylene-co-vinyl acetate
- Short Name
- EVA
- Name
- Polyethylene-co-vinyl acetate
- Group
- CTP - Commodity Thermoplastics
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
- (C2H4)n(C4H6O2)m
- Structural Formula
-
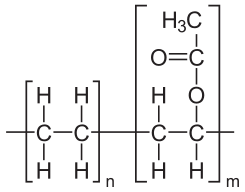
Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- -40 to +20 °C
- Melting Temperature
- 30 to 110 °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- 10 to 100 J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 345 to 360 / 470 to 480 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 7 to 120 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 160 to 200 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 2.3 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.35 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 0.92 to 0.95 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Semi-crystalline thermoplastic
- General properties
- High flexibility and toughness, good aging stability, high weather resistance, high gloss.
- Processing
- Injection moulding
- Applications
- Textile industry, hot melt adhesive, photovoltaic (embedding agent), agriculture and horticulture (films), cling films, shrink wrappings, shoe soles (VA-amount > 30 %)
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 10.65 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 8 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, piercec
- Atmosphere
- N2 (50 ml/min)
Evaluation
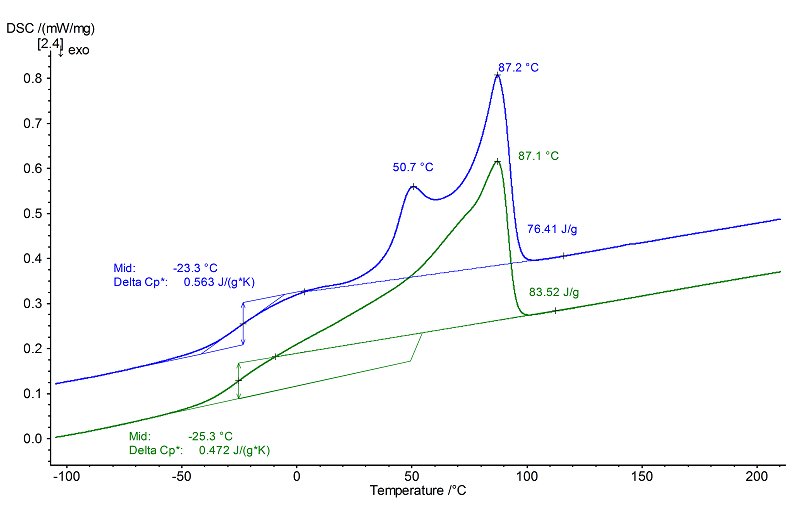
In the above graphics, only the 1st heating (blue) was evaluated since the effects in the 2nd heating − after controlled cooling – are no longer resolved.
In the 1st heating (blue curve), the glass transition occurs at -23°C (midpoint, with a change in specific heat of 0.56 J/(g·K)). It is followed by two overlapping, endothermal melting effects at 51°C and 87°C (peak temperatures). The entire heat of fusion of the combined peaks amounts to approx. 75 J/g.
In the 1st heating (blue curve), the glass transition occurs at -23°C (midpoint, with a change in specific heat of 0.56 J/(g·K)). It is followed by two overlapping, endothermal melting effects at 51°C and 87°C (peak temperatures). The entire heat of fusion of the combined peaks amounts to approx. 75 J/g.