PVC-U: Polyvinylchloride (without plasticizer)
- Short Name
- PVC-U
- Name
- Polyvinylchloride (without plasticizer)
- Group
- CTP - Commodity Thermoplastics
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
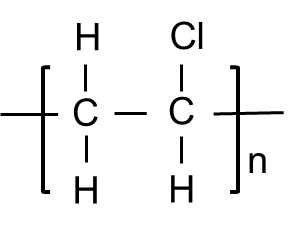
- Structural Formula
-
Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- 80 to 90 °C
- Melting Temperature
- - °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- - J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 285 to 315 / 460 to 475 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 2700 to 3000 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 60 to 80 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 0.84 to 1.17 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.13 to 0.29 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 1.38 to 1.55 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Amorphous thermoplastic
- General properties
- High mechanical stability, stiffness and hardness, good chemical resistance, good electrical and insulating properties, low tendency to stress cracking, good weatherability, low humidity absorption.
- Processing
- Extrusion, inject moulding, blow moulding, calendering, chip removing process.
- Applications
- Building industry (e.g. window profiles (with stabilizers), pipes), mechanical and apparatus engineering, electrical engineering, packaging industry.
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 10.82 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 5 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (40 ml/min)

Evaluation
Due to the missing plasticizer the glass transition of the entirely amorphous plastic PVC-U occurred at much higher temperatures, compared to PVC-P; in the present case at approx. 84°C (in both heatings, midpoint) with a step height (Δcp) of 0.32 J/(g·K) in the 2nd heating. The slight waves, overlapping the glass transition step in the 1st heating, are probably due to stress in the material that is dissipated during thermal treatment.