PLA: Polylactide
- Short Name
- PLA
- Name
- Polylactide
- Group
- CTP - Commodity Thermoplastics
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
- Structural Formula
-

Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- 45 to 65 °C
- Melting Temperature
- 150 to 160 °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- 93 to 140 J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 350 to 375 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 350 to 2800 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- - *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- - J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- - W/(m*K)
- Density
- 1.21 to 1.43 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Semi-crystalline thermoplastic
- General properties
- Good mechanical properties, low humidity absorption, high UV-resistance, low flammability.
- Processing
- Extrusion, injection molding, melt spinning
- Applications
- Fibres (yarns, textiles), packaging, agriculture and horticulture, medical engineering (e.g. suture material).
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 14.32 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 5 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (50 ml/min)
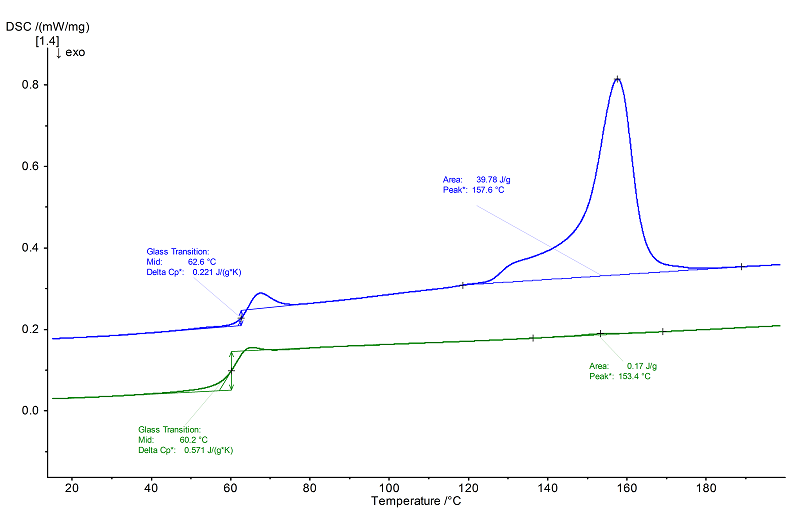
Evaluation
Polylactic acid showed a glass transition at 63°C in the 1st heating (midpoint, blue) which was overlapped by a relaxation peak as well as a melting peak between approx. 130°C and 180°C (peak temperature 158°C with a preceding shoulder). The following controlled cooling at 10 K/min was too quick for the material to crystallize. Therefore, only a very small melting effect at 153°C and a larger glass transition step (with a higher Δcp of 0.57 J/(g·K) compared to 0.22 J/(g·K) in the 1st heating) occurred in the 2nd heating due to the higher percentage of amorphous material.