SAN: Styrene-acrylonitrile copolymer
- Short Name
- SAN
- Name
- Styrene-acrylonitrile copolymer
- Group
- CTP - Commodity Thermoplastics
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
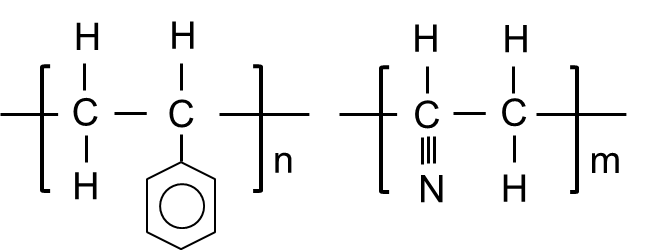
- Structural Formula
-
Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- 95 to 110/(125) °C
- Melting Temperature
- - °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- - J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 415 to 425 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 3500 to 3700 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 60 to 80 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 1.18 to 1.20 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.15 to 0.17 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 1.08 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Amorphous thermoplastic
- General properties
- High transparency, chemical resistance, high strength, high surface hardness, high scratch resistance.
- Processing
- Extrusion, injection moulding, thermoforming.
- Applications
- Transparent household goods, cosmetics packaging, medical components.
Internet Links
| Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Styrene-acrylonitrile_resin |
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 11.79 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 5 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (50 ml/min)
Evaluation
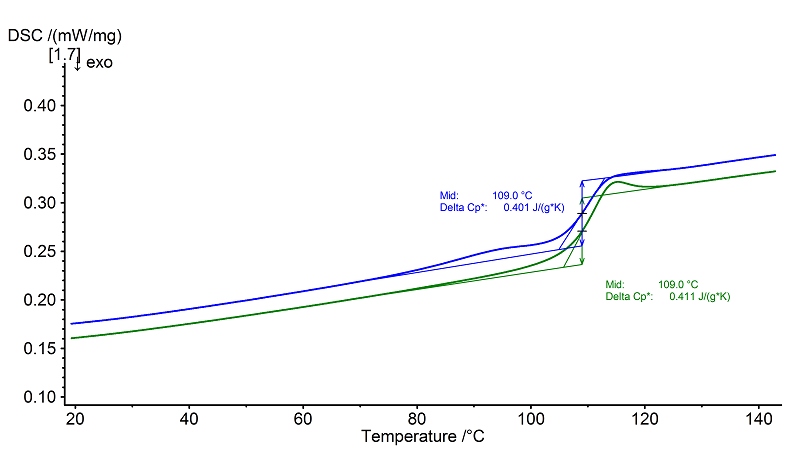
As an entirely amorphous thermoplastic, SAN has a glass transition in this case at 109°C (both heatings, midpoint each) with a step height (Δcp) of 0.40 J/(g.K) and 0.41 J/(g.K), respectively.
In the 2nd heating (green), the glass step shows a relaxation peak, indicating that short-range orders have formed in the polymer during the controlled cooling at 10 K/min. The thermomechanical history of the sample can be noticed in the DSC curve of the 1st heating (blue) by means of some slight waves.
In the 2nd heating (green), the glass step shows a relaxation peak, indicating that short-range orders have formed in the polymer during the controlled cooling at 10 K/min. The thermomechanical history of the sample can be noticed in the DSC curve of the 1st heating (blue) by means of some slight waves.