PA612: Polyamide 612
- Short Name
- PA612
- Name
- Polyamide 612
- Group
- ETP - Engineering Thermoplastics
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
- Structural Formula
-

Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- 40 to 65 °C
- Melting Temperature
- 210 to 220 °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- - J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 450 to 465 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 2100 to 2250 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 120 to 130 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 1.91 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- - W/(m*K)
- Density
- 1.06 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Semi-crystalline thermoplastic
- General properties
- High toughness. Very good resistance to fats, oils, fuels. Very good stress cracking resistance. Low coefficient of sliding friction. High abrasion resistance
- Processing
- Injection molding
- Applications
- Vehicle construction. Household items, e.g., toothbrushes. Plastic-rubber composites, e.g., for housing covers with seals
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 8.66 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 8 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (50 ml/min)
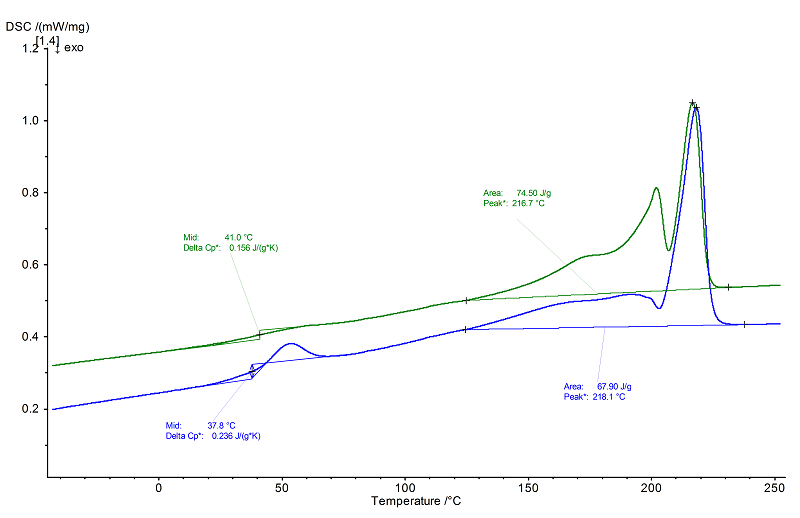
Evaluation
Shown in the 2nd heating (green) of this example is a broad, strongly structured endothermal melting transition with a distinctive pre-peak at 202°C and an additional shoulder at 173°C (peak temperatures). The temperature of the main effect (also peak temperature) occurred at 217°C. The total melting enthalpy was approx. 75 J/g.
The glass transition in the 2nd heating had a midpoint temperature of 40°C, at the lower end of the glass transition temperature for these materials. In the 1st heating (blue), the Tg midpoint was approximately 2 K lower and overlapped by a large
relaxation peak.
The glass transition in the 2nd heating had a midpoint temperature of 40°C, at the lower end of the glass transition temperature for these materials. In the 1st heating (blue), the Tg midpoint was approximately 2 K lower and overlapped by a large
relaxation peak.