PMMA: Polymethylmethacrylate
- Short Name
- PMMA
- Name
- Polymethylmethacrylate
- Group
- ETP - Engineering Thermoplastics
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
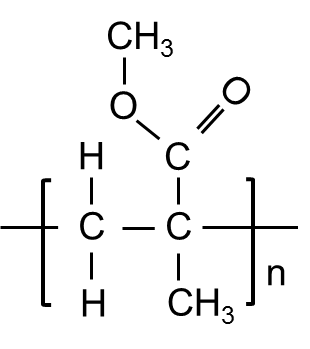
- Structural Formula
-
Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- 115 (synd.), 105 (atact.), 45 (isotac.) °C
- Melting Temperature
- - °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- - J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 360 to 390 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 3100 to 3300 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 90 to 110 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 1.45 to 1.47 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.16 to 0.25 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 1.15 to 1.19 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Amorphous polymer
- Identification
- High stiffness, high hardness. Very good translucence and light resistance. Good electrical insulation properties
- Processing
- Extrusion, injection molding, thermoforming, machining
- Applications
- Optics (e.g., eyeglasses). Automotive industry. Building industry
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 12.33 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 5 min/3 min/5 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (50 ml/min)

Evaluation
In the above DSC curve − typical for amorphous materials − a glass transition can be seen as a step in the endothermal direction with step heights (Δcp) of 0. 21 J/(g.K) (1st heating, blue) and 0.32 J/(g.K) (2nd heating, green) caused by the change in specific heat during transition from a glassy, brittle into a flexible, rubber-like state. The glass transition midpoint temperature occurs at 110°C in the 1st heating (blue) and at 109°C in the 2nd heating.