ASA: Acrylonitrile-styrene- acrylate copolymer
- Short Name
- ASA
- Name
- Acrylonitrile-styrene- acrylate copolymer
- Group
- CTP - Commodity Thermoplastics
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
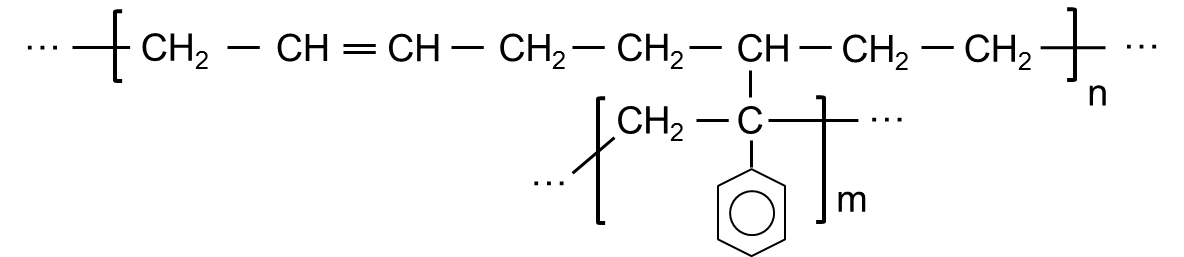
- Structural Formula
-
Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- -50 to -40 / 95 to 105 °C
- Melting Temperature
- - °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- - J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 415 to 425 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 2300 to 2900 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 85 to 105 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 1.3 to 1.4 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.17 to 0.19 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 1.04 to 1.07 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Amorphous thermoplastic
- General properties
- High impact strength and stability. High chemical stability, high gloss, high weatherability.
- Processing
- Injection molding,extrusion
- Applications
- Outer parts of vehicles. Thermalls stressed electrical devices, e.g.coffee machines and microwaves. Sport and leisure sector.
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 11.40 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 15 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (50 ml/min)
Evaluation
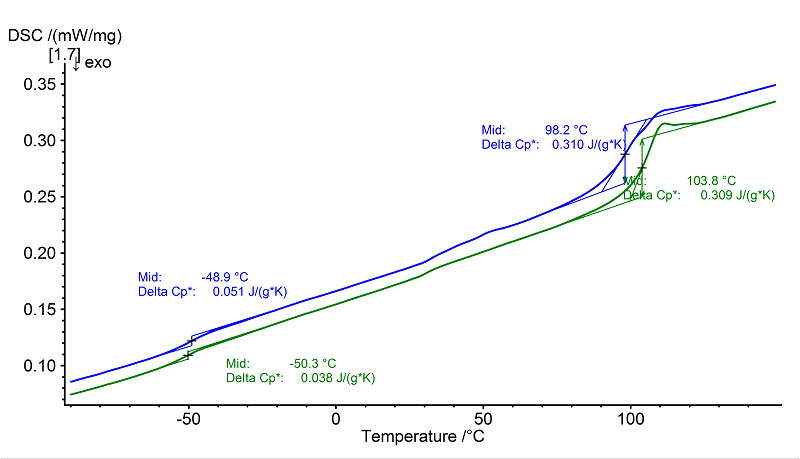
Two glass transitions can be seen in the above DSC curves. The first glass transition can be attributed to the acrylate component and occurs in the 2nd heating at -50°C (midpoint, green curve) with a change in specific heat of 0.04 J/(g.K)).
The second glass transition is due to the styrene component. The larger the relaxation peak, the more positively shifted the glass transition temperature to higher temperatures, as in this example.
The second glass transition is due to the styrene component. The larger the relaxation peak, the more positively shifted the glass transition temperature to higher temperatures, as in this example.