PEI: Polyetherimide
- Short Name
- PEI
- Name
- Polyetherimide
- Group
- HTRTP - High-Temperature Resistant Thermoplastics
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
- Structural Formula
-

Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- 215 to 230 °C
- Melting Temperature
- - °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- - J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 540 to 550 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 2900 to 3000 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 50 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- - J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.22 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 1.27 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Amorphous
- General properties
- High stability. High electrical impact strength. Good hydrolysis resistance. High UV and gamma ray resistance. Good resistance to stress cracking. Self-extinguishing
- Processing
- Injection molding, injection blow molding, extrusion, foaming
- Applications
- Electrics/electronics (e.g., housings, circuit boards). Aircraft construction (e.g., panels, coatings). Automobile industry. Medical engineering. Instrument and apparatus engineering
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 11.53 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 3 min/3 min/5 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (40 ml/min)
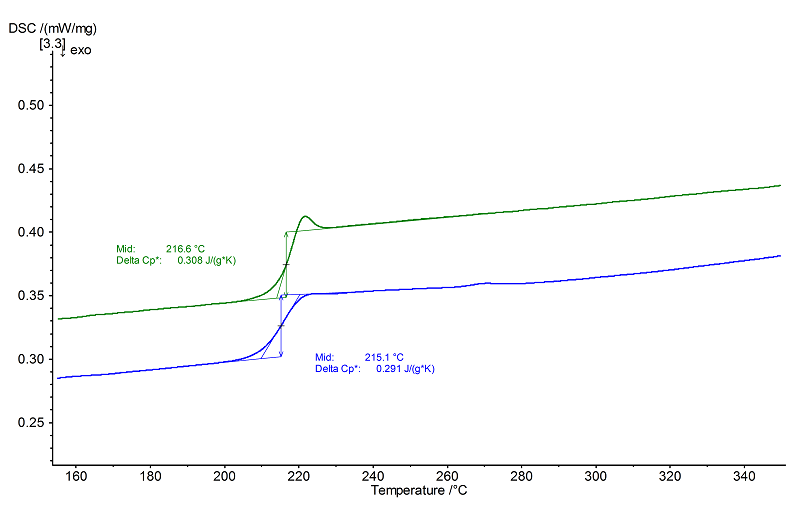
Evaluation
Polyetherimide (PEI) is completely amorphous and belongs to the high-temperature plastics, as reflected by the high glass transition temperature of approx. 217°C in the 2nd heating (green, midpoint) and 215°C in the 1st heating (blue). The glass transition in the 2nd heating is overlapped with a small relaxation peak. The controlled cooling at 10 K/min was probably far slower than the cooling rate employed during production of the polymer, causing the short-range order that was responsible for the endothermal relaxation peak.