PFA: Perfluoroalkoxy
- Short Name
- PFA
- Name
- Perfluoroalkoxy
- Group
- HTRTP - High-Temperature Resistant Thermoplastics
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
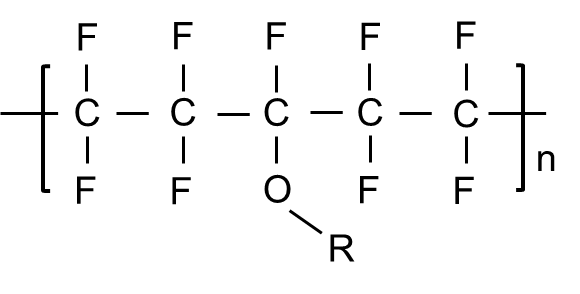
- Structural Formula
-
Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- - °C
- Melting Temperature
- 285 to 305 °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- 20 to 30 J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 353 to 550 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 800 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 120 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- - J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- - W/(m*K)
- Density
- 2.14 to 2.16 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Semi-crystalline polymer
- General properties
- Low friction value. High chemical resistance. Extremely low adhesion. Non-inflammability
- Processing
- Extrusion, injection molding
- Applications
- Hoses and fittings. Construction of chemical plants (corrosion-resistant lining). Nonstick coating, corrosion protection
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 16.07 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 5 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (40 ml/min)
Evaluation
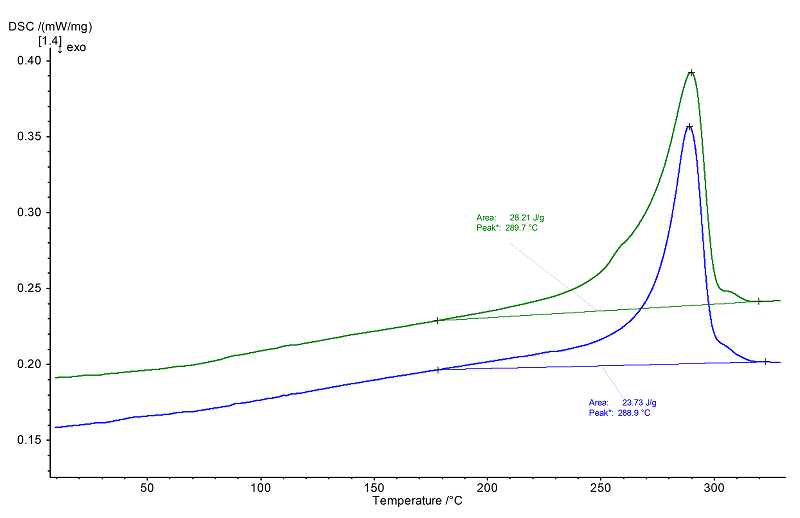
Although PFA belongs to semi-crystalline materials, in the present example only the melting transition is evident in the DSC curve with peak temperatures of 289°C (1st heating, blue) and 290°C (2nd heating, green). The absence of a glass transition signal indicates that the change in specific heat Δcp associated with the transition from the hard, brittle into the flexible state, is too small to be detected by DSC.