TPU: Urethane based TPE
- Short Name
- TPU
- Name
- Urethane based TPE
- Group
- TPEM - Thermoplastic Elastomers
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
- Structural Formula
-

Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- -50 to -30 °C
- Melting Temperature
- 135 to 220 °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- 3 to 15 J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 390 to 415 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 20 to 400 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 130 to 180 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 1.85 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.19 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 1.10 to 1.25 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Thermoplastic elastomer, block copolymer with hard and soft segments
- General properties
- High stability and flexibility. Good oil resistance. Good weather resistance (yellowing without property loss). High resilience
- Processing
- Injection molding, extrusion, blow molding
- Applications
- Automotive industry (damping elements, clutch elements). Medical engineering (bypass). Technical rubber articles (band conveyors, tooth belts, seals). Dashboards. Shoe soles
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 11.82 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 5 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (40 ml/min)
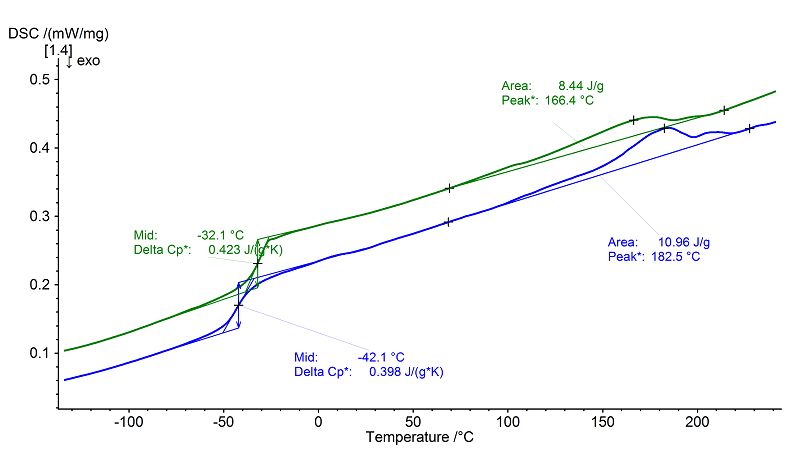
Evaluation
Presented in the above graphic is the 2nd heating of a TPU. Along with a glass transition at -32°C (Δcp 0.42 J/(g.K)), reflecting the thermal behavior of the soft segments, the DSC curve displays a broad endothermal effect (peak temperature of the main effect 167°C, heat of fusion approx. 8 J/g) that can be attributed to the melting of hard segments.