TPC: Ester-Ether based TPE
- Short Name
- TPC
- Name
- Ester-Ether based TPE
- Group
- TPEM - Thermoplastic Elastomers
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
- Structural Formula
-

Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- 0 to 60 °C
- Melting Temperature
- 190 to 230 °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- - J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 395 to 420 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 50 to 1000 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 165 to 200 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 1.90 to 2.22 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.10 to 0.19 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 1.0 to 1.2 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Thermoplastic elastomer, block copolymer with hard and soft segments
- General properties
- Good resistance to fuels and lubricating greases. Good hydrolysis resistance. Good abrasion resistance
- Processing
- Injection molding, extrusion, blow molding
- Applications
- Automotive industry. Technical rubber articles (belts, pulleys, O-rings, band conveyors). Electrical sector (e.g., cable sheathings, plug-in connectors). Shoe soles (soccer shoes)
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 12.13 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 8 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (40 ml/min)
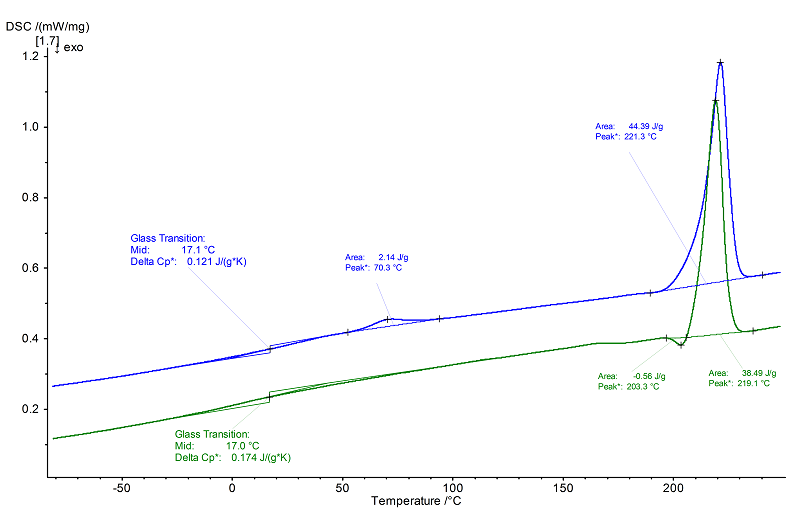
Evaluation
In the 2nd heating (green), the polymer first shows a glass transition at 17°C (midpoint, Δcp 0.17 J/(g.K)) and finally an endothermal melting effect (peak temperature 219°C, heat of fusion 38 J/g), directly preceded by an exothermal post crystallization (at 203°C with an enthalpy of 0.4 J/g). The peak temperature of the melting effect with 219°C in the 2nd heating is approx. 2 K lower than in the 1st heating (blue), due to the better contact between the sample and crucible bottom after the first melting.
The endothermal peak at 221°C in the 1st heating (blue) is also preceded by an although small post-crystallization at 192°C (see enlargement). The glass transition at 17°C (midpoint) is in good correlation with the behavior in the 2nd heating. Additionally, an endothermal effect at 73°C can be observed in the 1st heating (blue) that can be attributed to the melting of an additive, which is better distributed in the matrix after the first melting.
The endothermal peak at 221°C in the 1st heating (blue) is also preceded by an although small post-crystallization at 192°C (see enlargement). The glass transition at 17°C (midpoint) is in good correlation with the behavior in the 2nd heating. Additionally, an endothermal effect at 73°C can be observed in the 1st heating (blue) that can be attributed to the melting of an additive, which is better distributed in the matrix after the first melting.