PS: Polystyrene
- Short Name
- PS
- Name
- Polystyrene
- Group
- CTP - Commodity Thermoplastics
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
- (C8H8)n
- Structural Formula
-

Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- 80 to 105 °C
- Melting Temperature
- - °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- - J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 415 to 425 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 3100 to 3300 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 50 to 70 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 1.3 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.14 to 0.18 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 1.05 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Amorphous or semi-cristalline thermoplastic
- Identification
- transparant
- General properties
- Crystal clear and hard, Well resistant to aqueous bases and mineral acids
- Processing
- Injection and blow molding, Extrusion
- Applications
- Electrical engineering, Building industry (e.g. expanded polystyrene), Food industry (e.g., packaging), Consumer products for everyday use (e.g., CD covers, cloth hangers)
- Modifications
- Co-Po with PE, colored, Polymerfoam (EPS),
- Manufacturer
- Styrolution, Styron, Sabic, Nova Chemicals
Internet Links
| Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polystyrene |
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 12.36 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 5 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (40 ml/min)
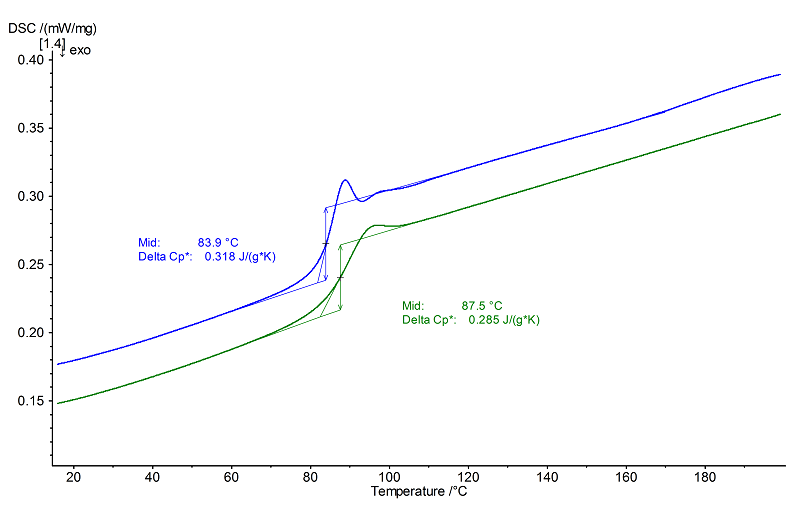
Evaluation
This example shows amorphous PS. Glass transition temperatures at 84°C (1st heating, blue, midpoint) and 88°C (2nd heating, green, also midpoint) were observed, each overlapped by relaxation peaks. The relaxation peaks are more distinctive in the
1st heating than in the 2nd heating. The 1st heating shows another small wave after the relaxation peak, indicating the elimination of additional stress.
The step heights (Δcp) were at 0.32 J/(g·K) (1st heating) and 0.29 J/(g·K) (2nd heating).
1st heating than in the 2nd heating. The 1st heating shows another small wave after the relaxation peak, indicating the elimination of additional stress.
The step heights (Δcp) were at 0.32 J/(g·K) (1st heating) and 0.29 J/(g·K) (2nd heating).