BR: Butadiene rubber
- Short Name
- BR
- Name
- Butadiene rubber
- Group
- EM - Elastomers
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
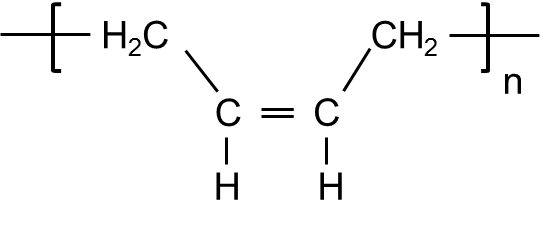
- Structural Formula
-
Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- -106 tp -95 (1.4 cis), -107 to -83 (1,4 trans), -15 (1,2) °C
- Melting Temperature
- -25 to 12 (1,4 cis), 97 / 145 (1,4 trans), 126 (1,2) °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- 46/170 (1,4 cis), 70 to 140 (1,4 trans) J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 370 to 385 / 460 to 475 °C
- Young's Modulus
- - MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- - *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 1.76 to 1.96 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.25 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 0.9 to 1.0 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Elastomer with hard and soft segments
- General properties
- High elasticity. High stability. High abrasion resistance
- Processing
- Extrusion, calendering, injection molding, vulcanization
- Applications
- Tire industry (blends with NR or SBR). Mechanical engineering. Technical rubber goods (e.g., band conveyors). Golf balls, shoe soles
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 12.29 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 8 min/3 min/8 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (40 ml/min)
Evaluation
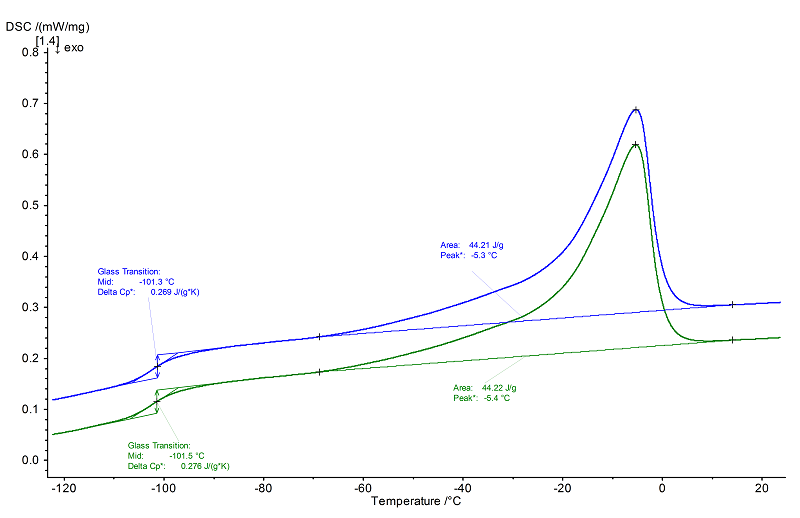
Polybutadiene or butadiene rubber has both soft and hard segments. For this reason, the above graphic shows a glass transition at -101°C (midpoint) in both heatings with a step height (Δcp) of approx. 0.27 J/(g.K) from the soft segments and a melting endotherm with a peak temperature of -5°C from the hard segments.
Based on literature data from the previous page (49 or 152), it can be concluded that the sample is mainly a 1,4 cis type.
Based on literature data from the previous page (49 or 152), it can be concluded that the sample is mainly a 1,4 cis type.