NR: Natural rubber
- Short Name
- NR
- Name
- Natural rubber
- Group
- EM - Elastomers
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
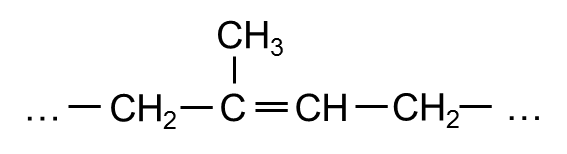
- Structural Formula
-
Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- -72 to -55 °C
- Melting Temperature
- 25 to 40 °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- 67 J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 375 to 400 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 1 to 5 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 180 to 260 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 1.91 to 2.08 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.13 to 0.15 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 0.91 to 0.93 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Amorphous rubber, partly with hard segments
- General properties
- High stability and high elasticity. High elongation at break. Good abrasion resistance
- Processing
- Cross-linking by means of sulfur incl. accelerator (e.g., mercaptobenzothiazole or sulfenamide) and activator (zinc oxide and stearic acid)
- Applications
- Tire industry. Technical rubber goods (e.g., rubber springs, band conveyors). Medical engineering. Toys. Shoe soles
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 13.00 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 7 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (40 ml/min)
Evaluation
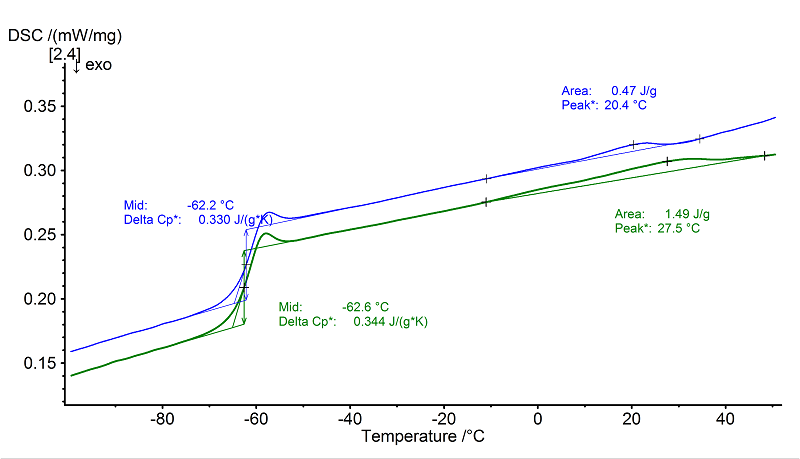
Natural rubber (NR) is mainly amorphous with a small amount of crystalline (hard) segments. This can be seen from the glass transition step at -63°C (2nd heating, green, midpoint) which is overlapped by an enthalpy relaxation, and from the shallow,
broad melting transition between -10°C and 50°C (peak temperature: approx. 28°C, 2nd heating) with a heat of fusion of only 1.5 J/g.
An even smaller melting enthalpy of 0.5 J/g was observed in the 1st heating (blue).
broad melting transition between -10°C and 50°C (peak temperature: approx. 28°C, 2nd heating) with a heat of fusion of only 1.5 J/g.
An even smaller melting enthalpy of 0.5 J/g was observed in the 1st heating (blue).