EP: Epoxy resin
- Short Name
- EP
- Name
- Epoxy resin
- Group
- TS - Thermosets
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
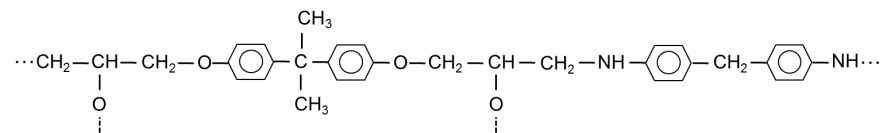
- Structural Formula
-
Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- 50 to 200 °C
- Melting Temperature
- - °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- - J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 380 to 450 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 3000 to 5000 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 60 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 1.67 to 2.10 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.17 to 0.52 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 1.15 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Thermoset
- General properties
- Good toughness. Good adhesion on many substrates. Good chemical resistance. Low cure shrinkage
- Processing
- Compression, spreading, injection processes such as RIM, VARI, RTM
- Applications
- Building industry (e.g., corrosion protection, sealings, floor coating). Boat building (construction adhesive). Electronics industry (circuit boards). Matrix for fiber-reinforced composites
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 13.22 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 5 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (40 ml/min)
Evaluation
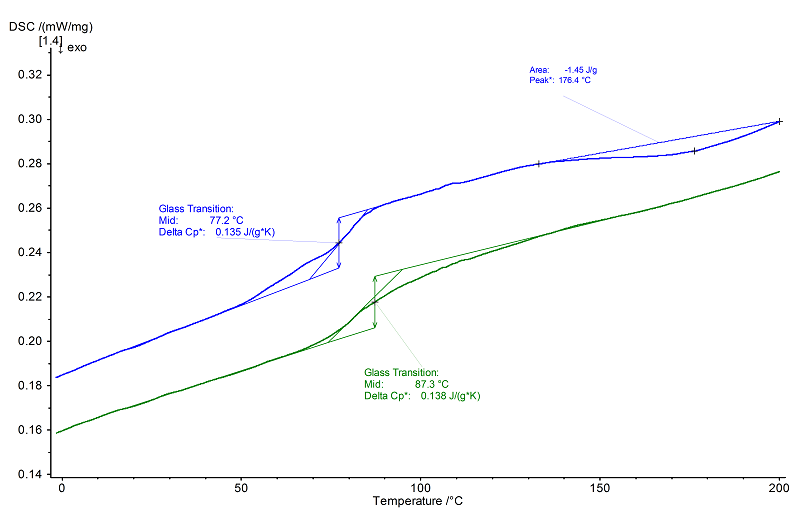
As an amorphous polymer, this epoxy resin exhibits a glass transition at 77°C (midpoint) with a specific heat capacity of 0.14 J/(g.K) in the 1st heating (blue) followed by an exothermal effect (peak temperature 174°C), due to post-curing of the resin. As a result of the post-curing, the glass transition temperature in the 2nd heating (green) is shifted to 88°C (midpoint).
The step height remains nearly the same. Since no further exothermal effect occurs, it can be assumed that the epoxy resin was entirely cured during the 1st heating.
Both the exothermal effect and the position (and shift) of the glass transition temperature to higher values can be interpreted as an evidence for the degree of curing of the material.
The step height remains nearly the same. Since no further exothermal effect occurs, it can be assumed that the epoxy resin was entirely cured during the 1st heating.
Both the exothermal effect and the position (and shift) of the glass transition temperature to higher values can be interpreted as an evidence for the degree of curing of the material.