PF: Phenol-formaldehyde resin
- Short Name
- PF
- Name
- Phenol-formaldehyde resin
- Group
- TS - Thermosets
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
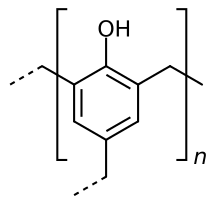
- Structural Formula
-
Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- 70 to 120 °C
- Melting Temperature
- - °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- - J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 450 to 555 °C
- Young's Modulus
- 5600 to 12000 MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 15 to 50 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 1.0 to 1.3 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- 0.35 to 0.70 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 1.40 to 1.80 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Thermoset
- General properties
- Very hard and stiff. Good chemical resistance. Low inflammability
- Processing
- Compression, injection molding, extrusion molding, transfer molding, foaming
- Applications
- Electrical industry (e.g., for circuit boards, plugs). Building industry (weather-resistant glue, for production of insulating materials). Vehicle construction. Matrix for fiber-reinforced composites
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 26.26 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 10 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 5 K/min/10 K/min cooling/20 K/min
- Crucible
- High-pressure steel crucibles, closed
- Atmosphere
- N2 (40 ml/min)
Evaluation
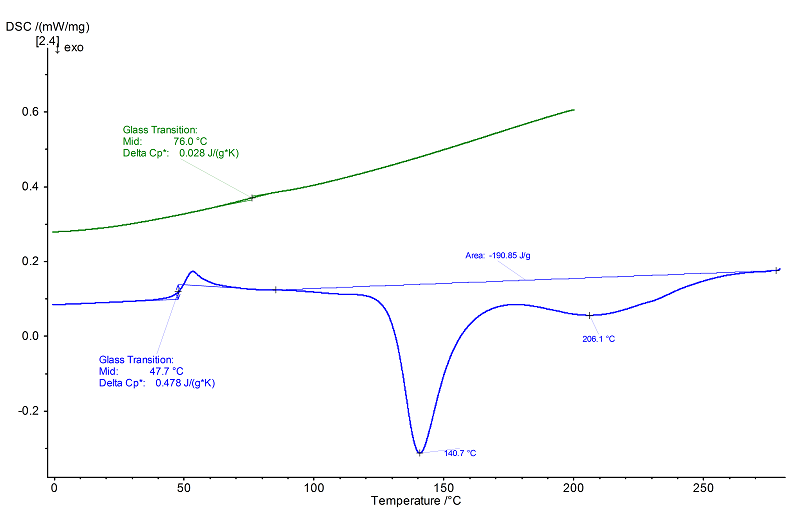
The 1st heating (blue ) shows a glass transition at approx. 48°C (midpoint) with an overlapping enthalpy relaxation, followed by a multi-step exothermal curing effect with peak temperatures of 141°C and 206°C and a total enthalpy of 191 J/g. In the
following 2nd heating (green), the glass transition shifted to approx. 72°C (midpoint) as a result of the extensive curing in the previous heating step.
following 2nd heating (green), the glass transition shifted to approx. 72°C (midpoint) as a result of the extensive curing in the previous heating step.