PUR: Polyurethane
- Short Name
- PUR
- Name
- Polyurethane
- Group
- TS - Thermosets
- General Properties
- Chemical Formula
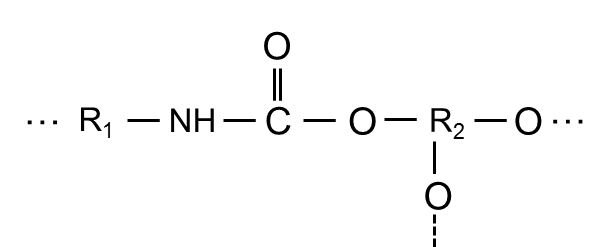
- Structural Formula
-
Properties
- Glass Transition Temperature
- 10 to 180 °C
- Melting Temperature
- - °C
- Melting Enthalpy
- - J/g
- Decomposition Temperature
- 240 to 350 °C
- Young's Modulus
- - MPa
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion
- 130 to 200 *10¯6/K
- Specific Heat Capacity
- 1.70 to 2.10 J/(g*K)
- Thermal Conductivity
- < 0.19 W/(m*K)
- Density
- 1.10 to 1.70 g/cm³
- Morphology
- Thermoset
- General properties
- Depending on the composition – the stiffness range expands from soft rubbers to technical plastics. Good abrasion resistance
- Processing
- Injection molding, foaming, coating
- Applications
- Automotive industry. Furniture industry. Building industry. Sports and leisure. Shoe industry (soles). Polyurethane paints and coatings. Casting compounds. Matrix for composites
Internet Links
NETZSCH Measurements
- Instrument
- DSC 204 F1 Phoenix®
- Sample Mass
- 18.95 mg
- Isothermal Phase
- 5 min
- Heating/Colling Rates
- 10 K/min
- Crucible
- Al, pierced
- Atmosphere
- N2 (40 ml/min)
Evaluation
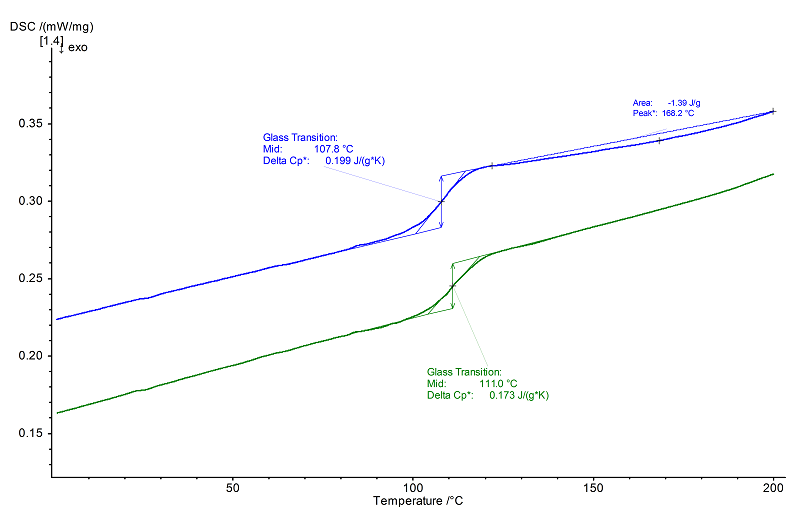
In the 1st heating, the glass transition at 107°C (midpoint) was followed by a broad, shallow, exothermal post-curing effect between approx. 120°C and 200°C (peak temperature 167°C). Due to the post-curing, the glass transition in the 2nd heating
(after controlled cooling) was approx. 4 K (midpoint temperature 111°C) higher.
The position of the glass transition temperature is directly related to the degree of curing.
The more extensive the post-curing, the more the glass transition shifts to higher temperatures.
(after controlled cooling) was approx. 4 K (midpoint temperature 111°C) higher.
The position of the glass transition temperature is directly related to the degree of curing.
The more extensive the post-curing, the more the glass transition shifts to higher temperatures.